Breaking the Ice: The Intricacies and Evolution of Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming, a mesmerizing fusion of ballet, gymnastics, and swimming, has a rich history and evolution. This sport challenges athletes to perform intricate routines while submerged in water, pushing their physical and mental endurance to the limit. Let's dive into the captivating world of synchronized swimming, examining its past, present, and potential future.
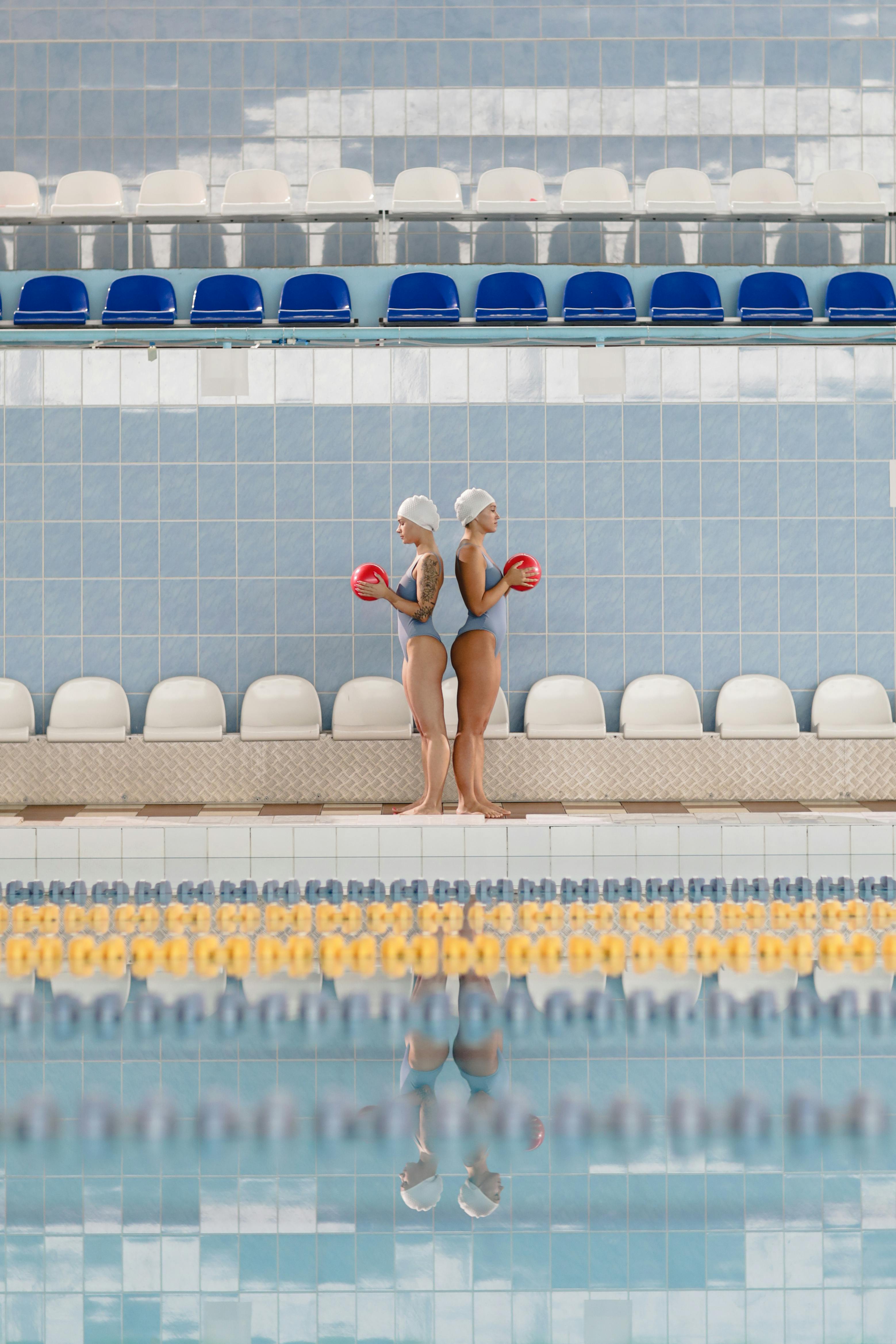

Origins and Evolution: The Birth of Aquatic Ballet
Synchronized swimming, originally known as “water ballet,” emerged in the late 19th century, inspired by the spectacular aquatic ballets of the World’s Fair events. Its development was propelled by pioneers such as Annette Kellerman, a famed Australian swimmer who popularized the sport with her mesmerizing underwater performances.
The early 20th century saw the introduction of synchronized swimming as a competitive sport. It was initially a male-dominated sport until women began making waves in the 1920s. By the mid-20th century, synchronized swimming had secured a spot in the Olympics, marking a significant milestone in its evolution.
Current Trends: The Art and Science of Synchronized Swimming
As the sport evolved, so did the complexity and intensity of routines. Today, synchronized swimming involves a blend of endurance, strength, flexibility, and precise timing. Athletes must maintain their positions, execute movements flawlessly, and stay afloat—all while holding their breath.
Recent trends have seen the sport becoming even more challenging. Teams are incorporating more acrobatic elements, demanding higher jumps and more complex underwater patterns. Furthermore, the use of music has become integral to routines, with swimmers moving in perfect harmony with the rhythm.
Training Techniques: Beyond Just Swimming
Training for synchronized swimming involves a rigorous regimen that extends beyond the pool. Athletes undergo cardiovascular and strength training to enhance their endurance and physical power. Flexibility exercises are crucial for executing intricate movements, while breath-holding exercises improve lung capacity.
The sport also demands mental fortitude. Athletes must be able to think quickly, memorize complex routines, and stay focused under pressure. Therefore, mental training techniques, such as visualization exercises, are equally crucial.
Synchronized Swimming in Practice: The Real-World Stage
The real-world application of synchronized swimming extends beyond the Olympic pool. It’s used in aquatic shows and entertainment performances worldwide, showcasing the sport’s beauty and complexity to a wider audience. Additionally, it’s increasingly recognized for its health and fitness benefits, making it a popular choice for recreational swimmers.
The Future of Synchronized Swimming: Elevating the Sport
Looking ahead, synchronized swimming is poised for exciting developments. Technological advancements could play a role in enhancing training methods and performance analysis. There’s also a growing push for gender inclusivity, with men’s and mixed duet categories introduced in World Championships.
In conclusion, synchronized swimming is an enthralling sport with a rich history and a promising future. As it continues to evolve, it remains a testament to the incredible feats of strength, endurance, and artistry that athletes are capable of achieving.